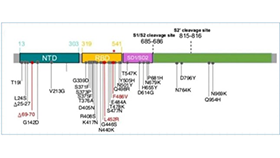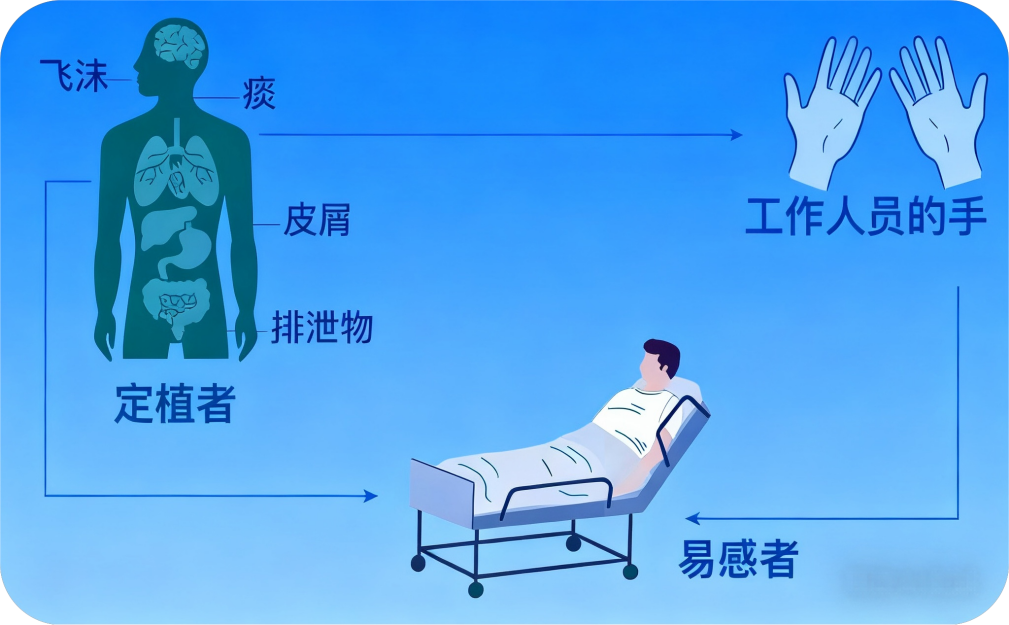
在外科临床实践中,手术部位感染(Surgical site infections,SSIs)作为术后常见且棘手的并发症,不仅延长患者住院时间、增加医疗负担,还可能导致手术失败、长期残疾甚至危及患者生命。其中,耐甲氧西林金黄色葡萄球菌(methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus ,MRSA)是引发高危手术如心脏外科、骨科手术SSIs的主要致病菌之一。国际权威指南已明确证实,术前 MRSA 去定植可显著降低感染风险,切实守护患者诊疗安全。
本文将结合《欧洲临床微生物学和传染病学会/欧洲感染控制委员会行为(ESCMID/EUCIC)临床指南》与《英国苏格兰重症监护病房患者中,通用型与目标型洗必泰联合莫匹罗星去定植策略的比较及表皮葡萄球菌血流感染的临床与分子流行病学研究》(2025)深入解析 MRSA 术前去定植的临床价值,MRSA 筛查的临床价值逐渐清晰,尤其在术前防控场景中展现出不可替代的作用。

引用文献:
[1] Righi E, et al. European Society of Clinical Microbiology and Infectious Diseases/European Committee on infection control clinical guidelines on pre-operative decolonization and targeted prophylaxis in patients colonized by multidrug-resistant Gram-positive bacteria before surgery. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2024 Dec;30(12):1537-1550.
[2] Popovich KJ, et al. SHEA/IDSA/APIC Practice Recommendation: Strategies to prevent methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus transmission and infection in acute-care hospitals: 2022 Update. Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol. 2023 Jul;44(7):1039-1067
[3] Sharaf S, et al. Universal versus targeted chlorhexidine and mupirocin decolonisation and clinical and molecular epidemiology of Staphylococcus epidermidis bloodstream infections in patients in intensive care in Scotland, UK: a controlled time-series and longitudinal genotypic study. Lancet Microbe. 2025 Aug;6(8)
文字 | 医学部
编辑 | 品牌宣传部
图片 | 来源于伯杰医疗
















.jpg)